|
Artificial Intelligence of Things (AIoT) systems, which seamlessly merge sensing capabilities with artificial intelligence for IoT devices, have empowered a new generation of smart applications in several important sectors, including transportation and healthcare. According to Markets and Markets, the global AIoT market is projected to grow to $16.2 billion by 2024, boasting a compound annual growth rate of 26.0%. However, AIoT systems pose a set of new critical challenges. First of all, many of these systems are mission-critical and time-sensitive, which means that computing and communication tasks must be completed within tight timeframes. Second, the massive amount of data produced often needs to be processed on resource-constrained devices. Finally, it can be challenging to integrate this highly complex data coming from multiple sensing modalities.
The AIoT Lab in the Department of Information Engineering has developed new world-class artificial intelligence and sensing technologies at the frontiers of smart traffic, healthcare, mobile sensing, and Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS). The director, Prof. Guoliang Xing, is a Professor and an IEEE Fellow who has received multiple honours, including the Withrow Distinguished Scholar Award from Michigan State University and the CAREER Award from the US National Science Foundation. The co-director, Prof. Zhenyu Yan, is a Research Assistant Professor who has received the Rising Star Award from ACM SIGBED China and the Kan Tong Po International Fellowship from the UK Royal Society. In the last three years, the lab’s cutting-edge work on AIoT systems has received six Best Paper/Poster Awards and Finalist recognition from various top international conferences.
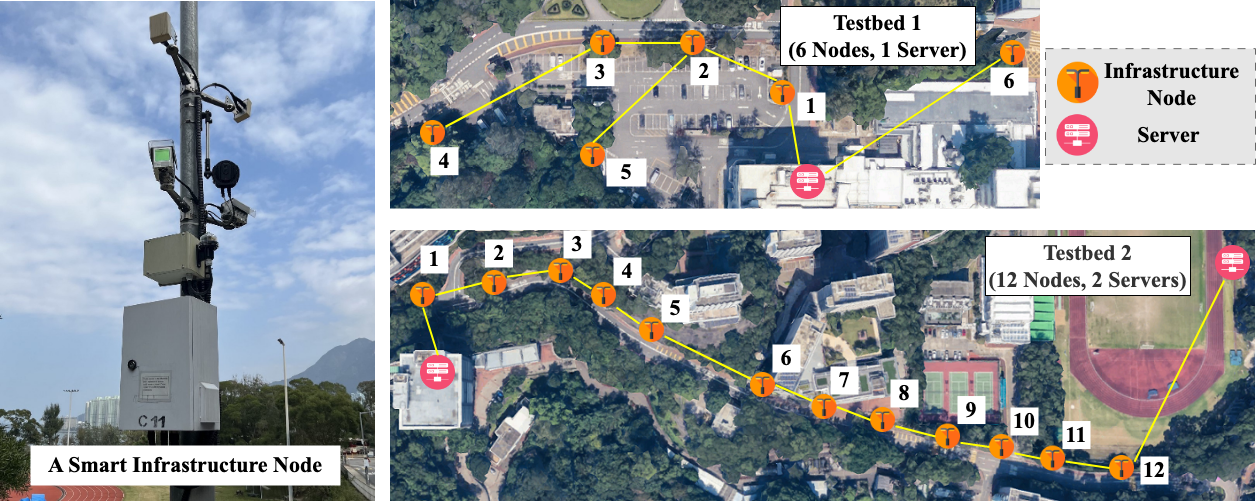
The Largest Campus Testbed on Intelligent Roadside Infrastructure
Transport services made up 41.8% of Hong Kong’s service exports in 2021. However, accidents, pollution, and increasingly congested roads remain the greatest transportation pain points. Although autonomous driving presents a safe, clean, and efficient technology that could revolutionise transportation, a robust solution for urban environments has yet to be realised. In recent years, we have witnessed the emergence of a new paradigm that leverages intelligent road systems to enhance the limited capabilities of both human-driven and autonomous vehicles. The CUHK AIoT lab has built Hong Kong’s largest campus testbed of intelligent roadside infrastructure. By enhancing more than 20 existing lampposts with additional sensors (such as LiDAR, thermal cameras, and mmWave radar), computing, and wireless communication capabilities, test vehicles are able to obtain more accurate and comprehensive contextual awareness and driving assistance. For example, the augmented infrastructure can significantly reduce blockage of vehicles’ field of view. CUHK AIoT lab has already published several papers on this project and presented the findings at top international conferences, and received the Best Paper Award Runner-up at ACM MobiCom 2022 in Sydney, Australia.
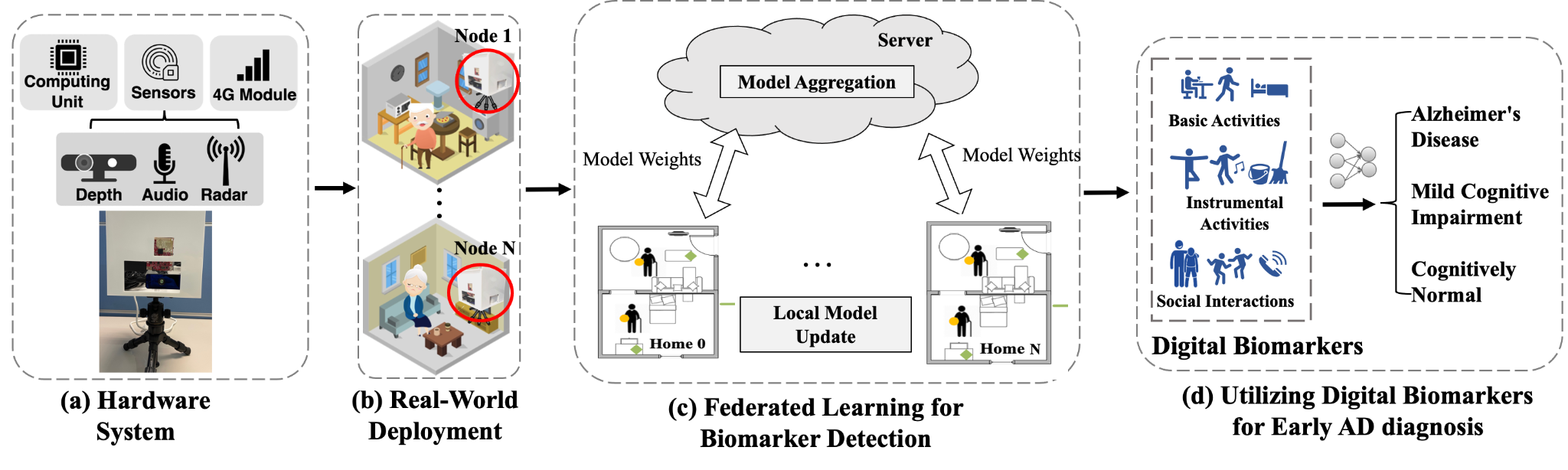
The First Multidimensional Digital Biomarker Detection System for Alzheimer’s Disease
Another key global challenge today is delivering high-quality yet economically efficient healthcare solutions. The prominence of mobile devices and recent breakthroughs in machine learning have enabled an emerging class of AI-powered mobile health systems, which could transform today’s reactive healthcare practices towards more proactive and individualised care for enhanced well-being. The CUHK AIoT Lab and CUHK Faculty of Medicine have built the first end-to-end Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) monitoring system that integrates multi-modal sensors and federated learning algorithms for detecting multidimensional digital biomarkers in natural living environments. The team has developed a compact multi-modality hardware system that can function for several months in home environments. On top of the hardware system, the team has designed a multi-modal federated learning system that can accurately detect more than 20 digital biomarkers in real-time while preserving privacy. The system has been deployed in a four-week clinical trial involving more than 60 elderly participants, including AD, mild cognitive impairment, and cognitively normal subjects. The system built by the AIoT Lab offers a new clinical tool that allows medical researchers and professionals to monitor the progression of AD manifestations and study the complex correlation between multidimensional interpretable digital biomarkers, demographic factors of patients, and AD diagnosis in a longitudinal manner.
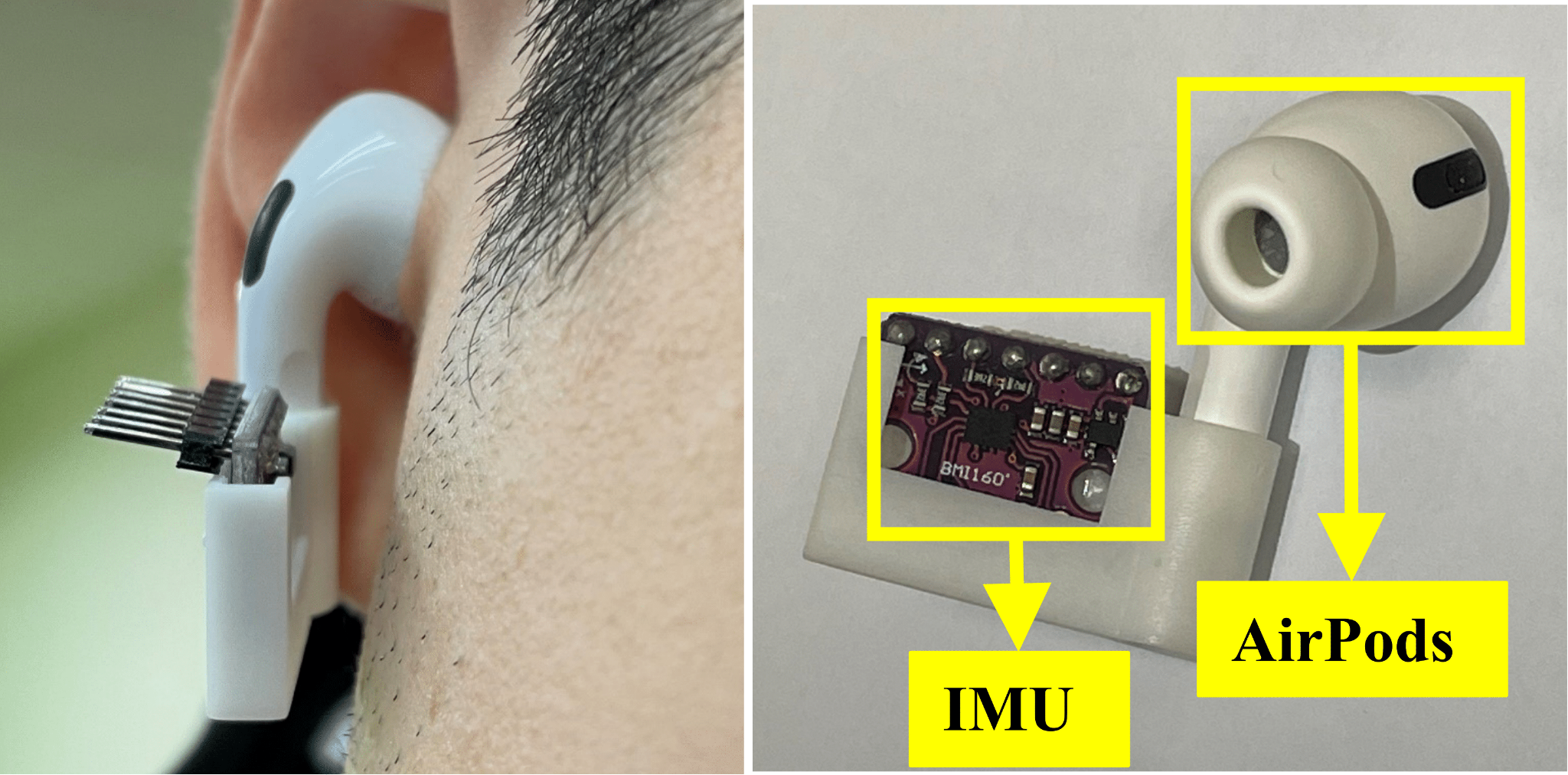
Earables, An Emerging Platform For Ubiquitous Sensing
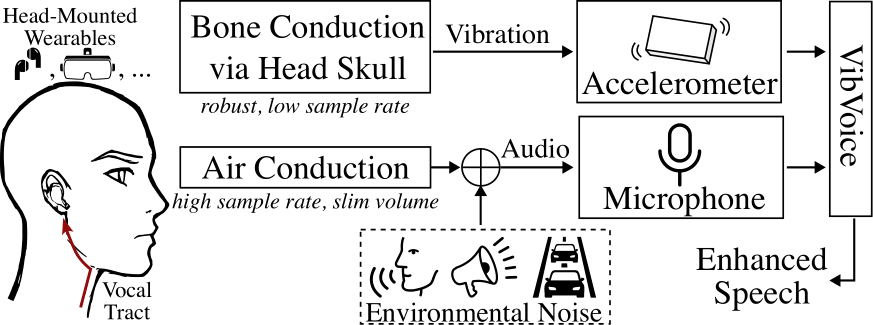
Earables, or ear-worn devices, have become a new generation of mobile computing and sensing platforms. With the popularisation of true wireless stereo (TWS) earphones like Apple AirPods and Samsung Galaxy Buds, earables have grown into the largest category of wearable devices. Since earables have direct contact with the head, and include on-device sensors like inertial measurement units (IMU) and microphones, they enable diverse applications such as spatial audio, acoustic noise cancellation (ANC), and health monitoring. CUHK AIoT Lab has developed a novel earable sensing platform that can collect multi-modal data on the user’s head as TWS earphones. The team has found that the vibration conducted from the head bone contains clean speech from the user without environmental noise. VibVoice, a novel speech enhancement approach for earables, was developed after extensively measuring the bone conduction transformation between speech and head vibration. VibVoice can reconstruct clean speech from bone-conducted vibrations with limited bandwidth and achieve good performance over state-of-the-art speech enhancement algorithms on popular TWS earphones.
|
